Our eyes are in many cases thought about the windows to the world, permitting us to encounter life in striking tones, shapes, and subtleties.
An eye center is a specific clinical office that spotlights on the finding, treatment, and the board of eye infections and vision problems.
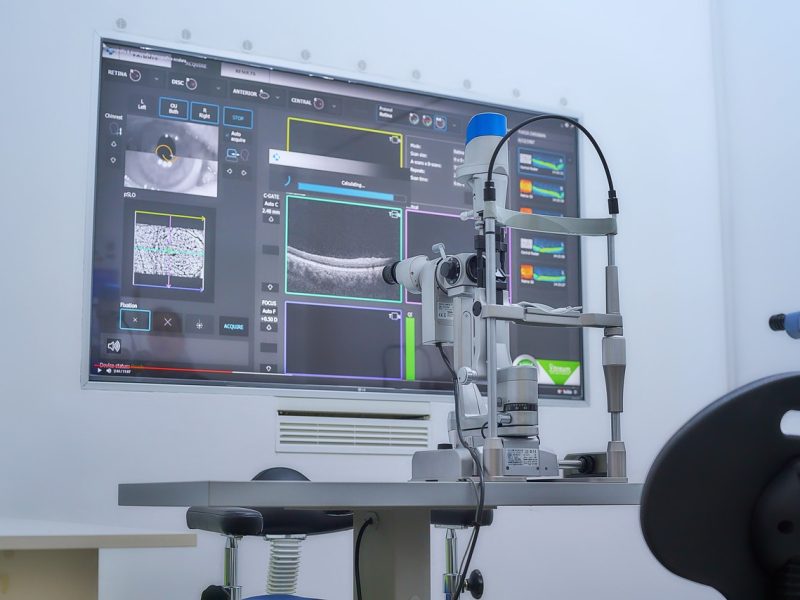
These administrations range from customary eye tests to medical procedures for complex eye conditions.
They can deal with conditions like waterfalls, glaucoma, macular degeneration, and retinal infections.
Ophthalmologists are prepared to analyze and treat a wide assortment of eye conditions, carry out procedures, and endorse prescriptions.
These are clinical specialists (MDs) who have practical experience in eye care.
Nonetheless, they don't carry out procedures. They frequently allude patients to ophthalmologists for cutting edge medicines.
Opticians are experts who help with fitting and apportioning eyeglasses and contact focal points in view of solutions from ophthalmologists or optometrists. While they don’t analyze or treat eye sicknesses, they assume a pivotal part in assisting patients with finding the right eyewear.Eye facilities are staffed by ophthalmologists, optometrists, and other eye care experts who cooperate to offer thorough types of assistance pointed toward protecting or working on the wellbeing of the eyes. Get more detail about synstest kristiansand.

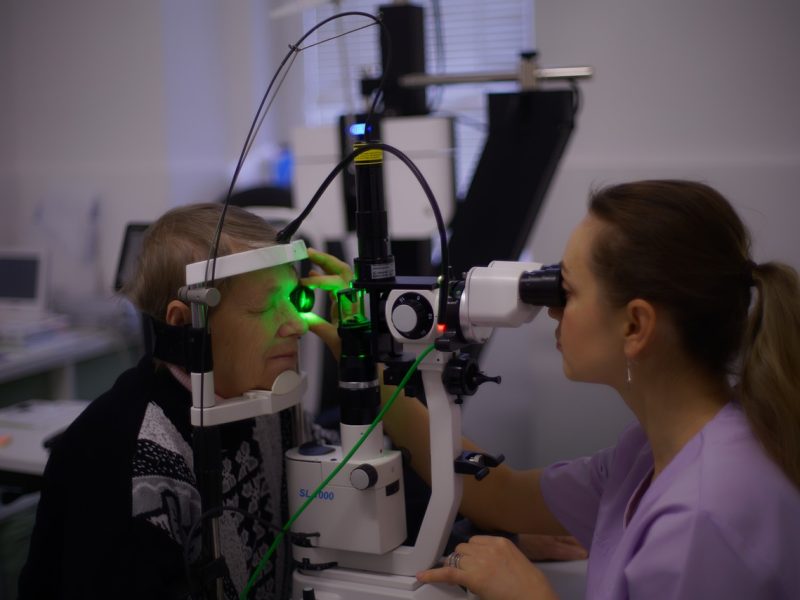
Optometrists (ODs) are eye care experts who give vision care administrations, including eye tests, recommending glasses and contact focal points, and diagnosing normal eye conditions. In a few particular facilities, orthoptists are engaged with diagnosing and treating conditions connected with eye developments and binocular vision, like strabismus (crossed eyes) or amblyopia (sluggish eye). Learn more and get information about briller kristiansand .
Treatment choices incorporate remedy glasses, contact focal points, and refractive medical procedure like LASIK.
Age-related trouble in zeroing in on close to objects, frequently requiring bifocals.
An eye facility tends to an extensive variety of eye medical problems, both normal and uncommon.
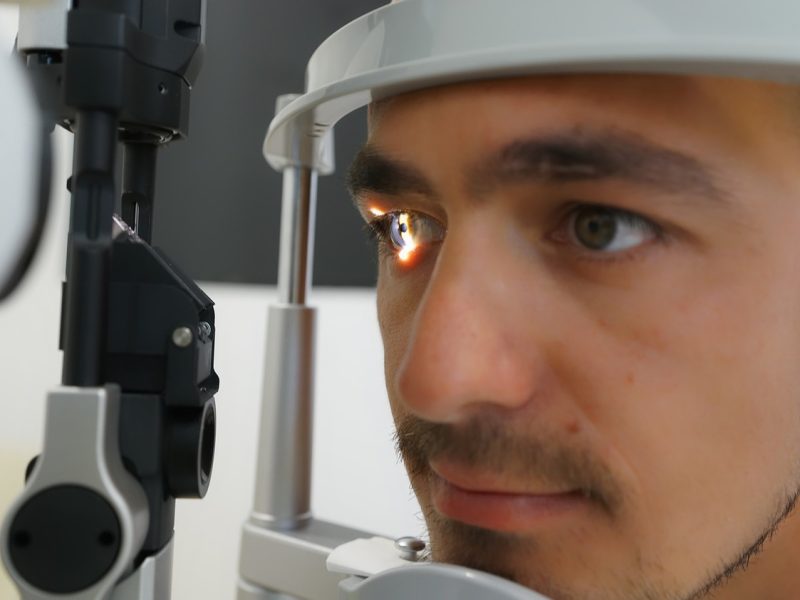

A gathering of eye sicknesses that cause harm to the optic nerve, frequently connected with high intraocular pressure. Whenever left untreated, glaucoma can prompt super durable vision misfortune. Early identification through customary eye tests is vital, as glaucoma can be made do with meds or medical procedure.
A condition where the eyes don’t deliver an adequate number of tears or the right nature of tears to keep the eyes wet. It can cause distress, aggravation, and even harm to the outer layer of the eyes. Treatment choices incorporate fake tears, solution eye drops, or way of life changes. Eye facilities additionally deal with contaminations like conjunctivitis (pink eye), as well as irritation related conditions, for example, uveitis, which influences the center layer of the eye. Find more about brillerogiris here.
Conditions like retinal separation, diabetic retinopathy, and macular degeneration are treated by experts in retinal wellbeing. Early conclusion and treatment are fundamental to forestall extremely durable vision misfortune.